Integrating Azure Arc with the Flux GitOps extension presents a highly effective approach for deploying infrastructure and applications to Kubernetes. In a previous article, I provided a comprehensive guide on installing the Flux extension and configuring deployments using Kustomize and YAML files, which can be found here.
Today, I want to demonstrate the process of deploying Helm charts using Azure Arc in conjunction with the Flux GitOps extension.
This post is part of “Azure Arc Series - Manage an on-premises Kubernetes Cluster with Azure Arc”.
Understanding Helm
When it comes to deploying microservices on Kubernetes, especially those with dependencies, the process can often be complex. This is where Helm, a powerful package manager for Kubernetes, proves invaluable. Helm simplifies the deployment process by enabling the creation of packages, with Helm taking charge of installation and updates. These packages, known as charts, encompass all the necessary components and configurations required by your application. Leveraging Helm’s capabilities, you can effortlessly create or update your application based on the provided chart. Furthermore, Helm also functions as a versatile template engine, facilitating easy configuration of charts, be it locally or within your CI/CD pipeline.
For further insights and details, I recommend referring to my earlier post, Helm - Getting Started.
Understanding the Flux Helm Controller
The Flux Helm Controller, an integral component of the Flux installation, is automatically installed alongside the Flux GitOps extension (specifically, the microsoft.flux extension) in Azure Arc. As a result, there’s no need to install any additional tools to facilitate the deployment of Helm charts.
The Flux Helm Controller serves as a management tool for Kubernetes applications and cluster resources. It seamlessly integrates with the Helm package manager, enabling a GitOps workflow for deploying, updating, and rolling back Helm charts (which encapsulate Kubernetes application packages) within a cluster.
By leveraging the Flux Helm Controller, developers can define the desired state of their applications within a Git repository. The controller then ensures that the actual state of the cluster aligns with this desired state. It automatically monitors Git for any changes and promptly updates the cluster to maintain the desired state.
It’s worth noting that Helm charts can be deployed from both Git repositories and Helm repositories. For the purpose of the upcoming demonstration, a Git repository will be utilized. However, in an upcoming post, I will elaborate on deploying charts from Helm repositories. To gain further insight, refer to the architectural depiction of the Flux Helm Controller presented in the accompanying screenshot.
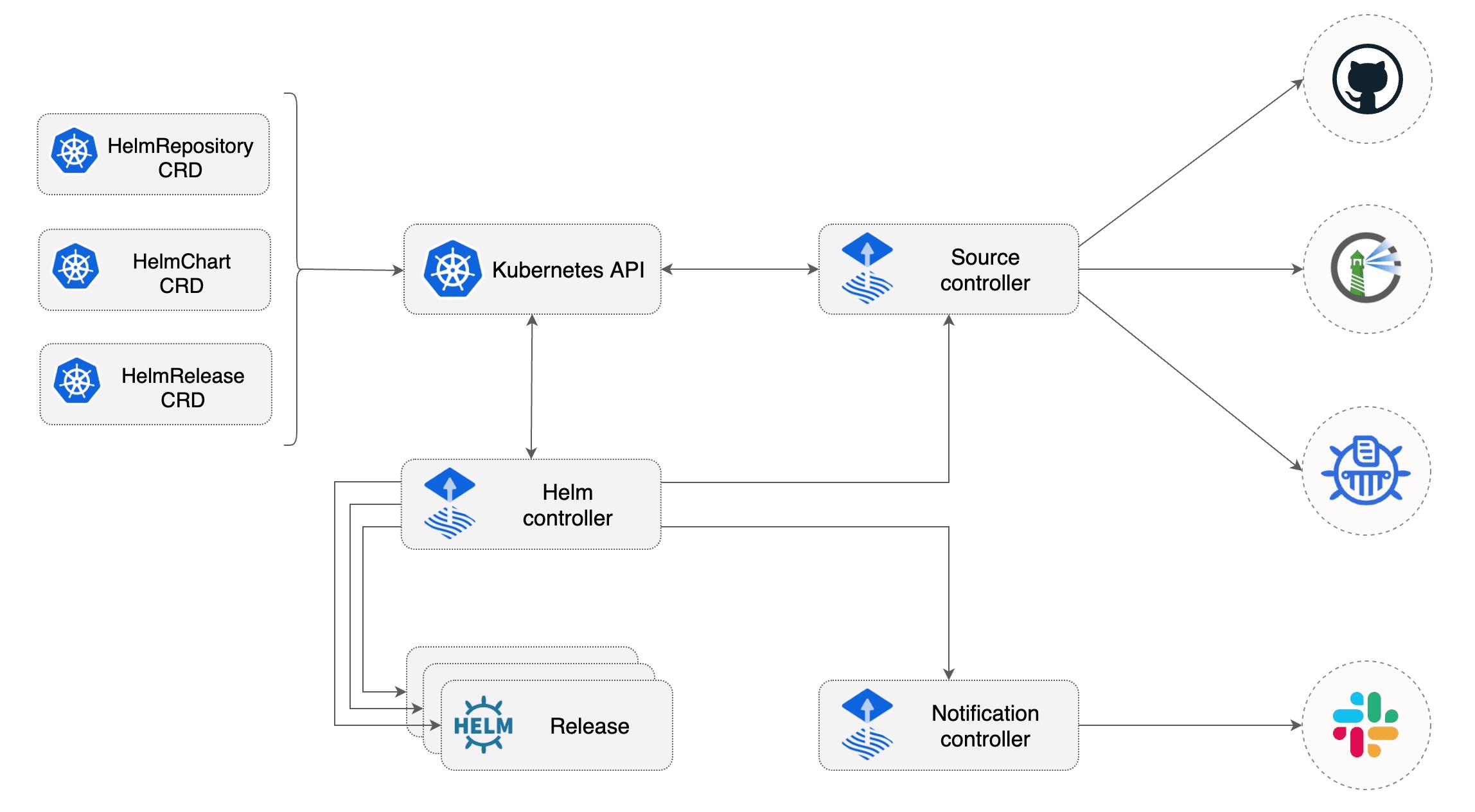
Flux Helm Controller Architecture (Source)
Deploy Helm Charts from a Git Repository
You can find the code of the demo on GitHub.
Deploying a Helm chart directly from your Git repository offers a straightforward approach. To begin, create a new YAML file where you’ll define essential details such as the path to your Helm chart within the Git repository, the branch to track, polling interval, and a name for the deployment.
Take note of the line “clusterconfig.azure.com/use-managed-source: “true”, which informs Flux that the Helm chart is stored within a Git repository.
The next file to create is the kustomize file, which instructs the GitOps operator regarding the files it should execute. In the kustomize file, include the name of the previously generated YAML file.
Ensure that both files reside within the same folder in your Git repository. If you navigate to my GitHub repository, you will find these files within the ArcHelmGitOps folder. If you look at my GitHub repo, you will find the files in the ArcHelmGitOps folder.
Testing the Helm Chart Deployment from a Git Repository
Before proceeding with deploying your application using the Azure Arc GitOps extension, ensure that you have Azure Arc installed on your Kubernetes cluster.
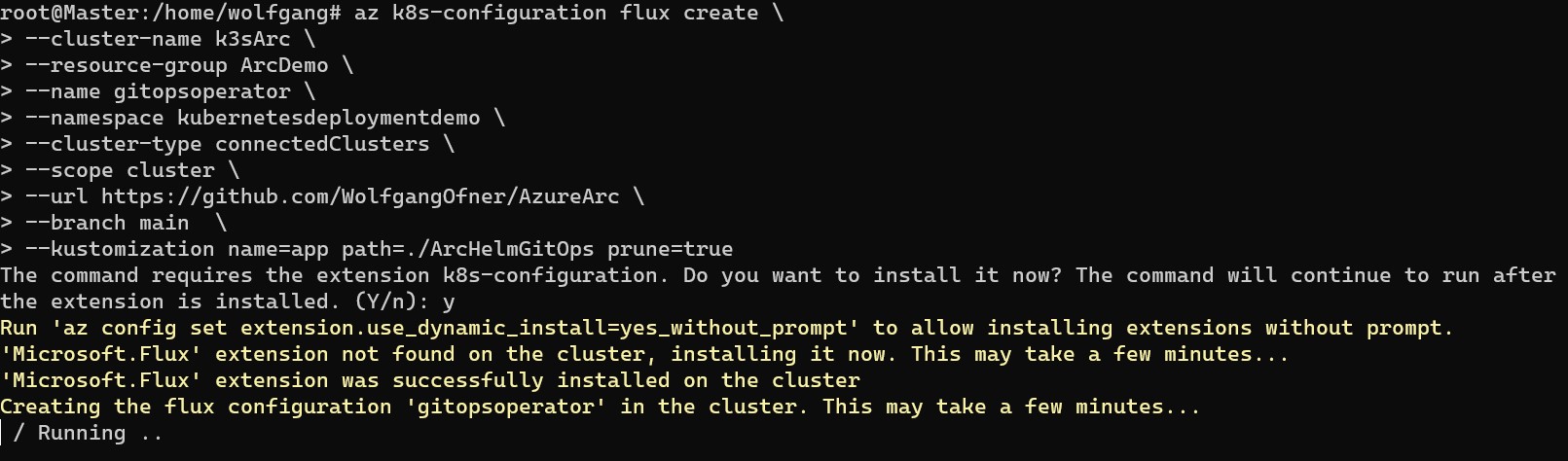
Once Azure Arc is successfully installed, proceed to install a GitOps operator with the following command:
This command will install the GitOps extension and subsequently the operator. The provided parameters should be self-explanatory.
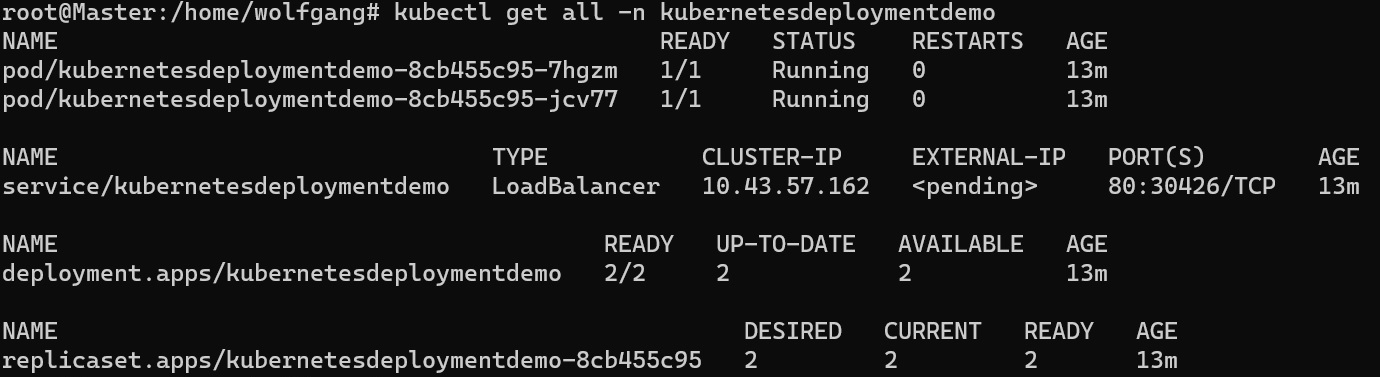
After a few minutes, your application should be up and running within your k3s cluster.
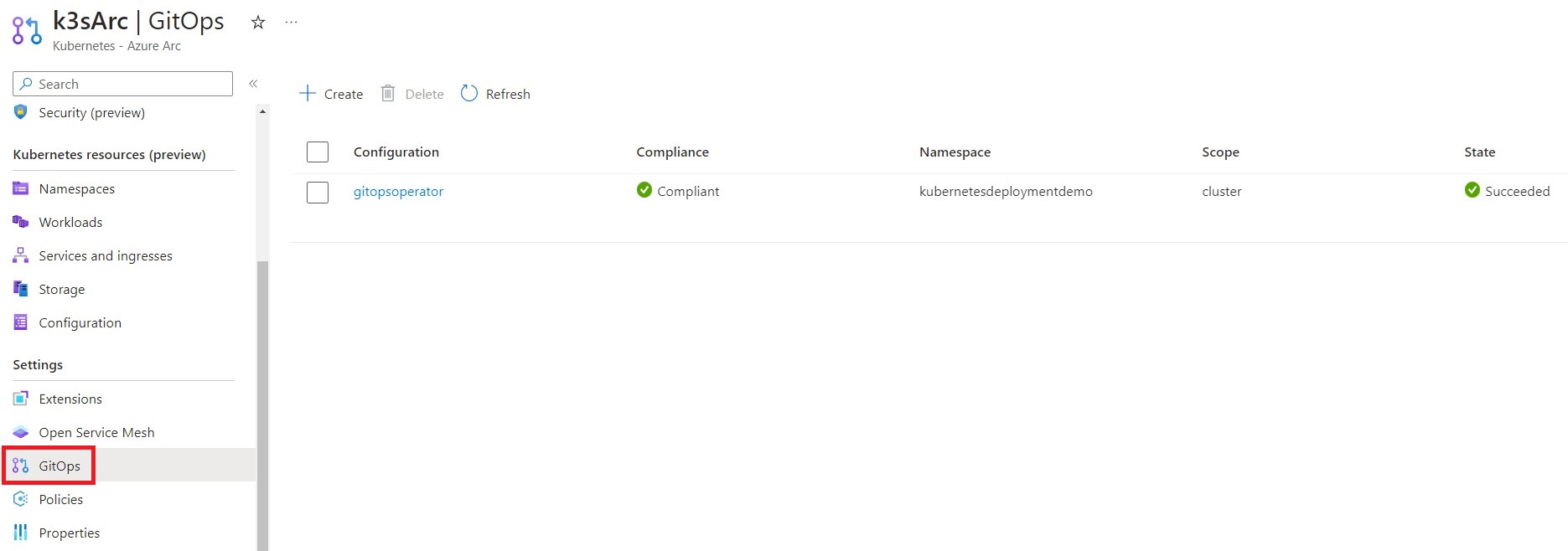
Additionally, you can verify the compliance and state of the GitOps operator in the Azure portal. Access your Azure Arc instance, navigate to the GitOps pane, and observe the Compliance status as “Compliant” and the State as “Succeeded”.
Overriding Values in the values.yaml File
In typical Continuous Deployment (CD) pipelines, it is common to override values, such as the image tag, in the values.yaml file. However, in the absence of a deployment pipeline utilizing GitOps, alternative methods are required for value overrides. Fortunately, it is possible to achieve this by adding the desired values directly to the HelmRelease file. The following code snippet demonstrates how to override the value for replicaCount and set it to 2:
By specifying the desired values directly within the HelmRelease file, you can conveniently override specific values without relying on a traditional CD pipeline (I will update this file with a CD pipeline in a future post). Customize the replicaCount and add any other necessary value overrides as need.
Updating or Deleting the Flux Configuration
Thus far, we have focused on creating a new flux configuration. However, there are various other operations that can be performed, including updating or deleting an existing configuration. For a comprehensive overview of all available commands, please refer to the documentation.
If you have completed the demo and wish to remove the flux configuration, execute the following command:
To uninstall the Flux extension, utilize the subsequent command:
Conclusion
In conclusion, Azure Arc combined with the Flux GitOps extension provides a powerful solution for deploying applications to Kubernetes clusters. Leveraging Helm and the Flux Helm Controller, developers can simplify the deployment process and maintain the desired state of their applications. With the ability to deploy Helm charts from Git repositories and easily manage configurations, Azure Arc and Flux enable efficient management of Kubernetes deployments, promoting collaboration and operational efficiency. Embracing these tools empowers developers to streamline their deployment workflows and maximize the potential of their Kubernetes infrastructure.
In my next post, I will explore the installation of Helm charts from a Helm repository, aiming for a smoother experience compared to the demo discussed today. Stay tuned as we dive into this process and uncover its potential benefits.
You can find the code of the demo on GitHub.
This post is part of “Azure Arc Series - Manage an on-premises Kubernetes Cluster with Azure Arc”.


Comments powered by Disqus.